


The installed packages will appear in a separate block (“Installed Groups”): Yum groupinstall "System Administration Tools"
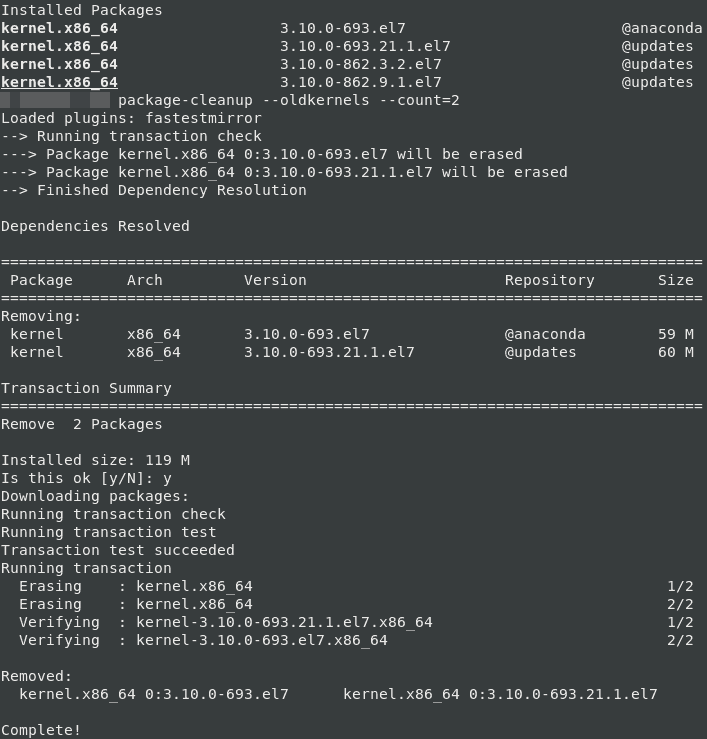
You can install the group list using this command: Yum groupinfo "System Administration Tools”Īs you can see, the list contains the monitoring and debugging tools. Here is another useful group list – “System Administration Tools”: To learn more about the group and its packages:Īfter the check we see that the set of packages and services for a web server will be installed. Let’s see how it works on the example of the “Basic Web Server” list. You can display the list of these groups: There are some predefined package groups with different program sets in the repository. You can also use the group installation of packages with grouplist. You can roll back to the previous package version using yum: For example, your site has stopped working after you had updated php version. In some cases, issues may occur after you have updated a package or a service. To get information about available security updates: You can check if there are any available updates for your system with the following command: To update all installed packages, run this command: For example, look for the Squid proxy package: Using the provides option, you can find packages containing the specific file. To find a package by its name or description: To remove an installed package with yum, the remove parameter is used:īefore you remove any package, it is recommended to check its dependencies (there are packages that cause the removal of some other packages when you try to remove them). Yum can install multiple packages at once:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
